Table of Contents
Great systems are not just built. They are monitored.
MetricFire is a managed observability platform that helps teams monitor production systems with clean dashboards and actionable alerts. Delivering signal, not noise. Without the operational burden of self-hosting.
Introduction
Looking to visualize your Elasticsearch data with Grafana? This tutorial walks you through setting up Grafana and Elasticsearch using Docker, connecting data sources, and building insightful dashboards for log and metric monitoring.
What is Grafana?
Grafana is a very versatile visualization tool. It is able to read data from a variety of data sources and plot with many different visualization options, such as graphs, gauges, world maps, heatmaps, and more. Check out our articles on Grafana dashboards and our comparison of Grafana and Kibana.
MetricFire offers a Hosted Grafana solution, so you can try it for yourself on the MetricFire free trial! You can also book a demo and talk to us directly about what MetricFire can do for you.
What is Elasticsearch?
Elasticsearch is an open-source, distributed data store for analyzing and searching data. Elasticsearch uses JSON-based document structure to store and index data. It uses a data structure called an Inverted Index to enable a very fast search on the stored data. Many firms use Elasticsearch to power their search across their databases.
MetricFire is a hosted Grafana service where our engineers can set up any Grafana plugins for our customers upon request, with this service included in all packages. Check out how to do it below, and if you're looking to offload that work, sign up for our free trial.
Additionally, be sure to check out our Hosted Graphite services. Our Hosted Graphite services offer three times the redundant storage (beyond the default Graphite storage), API-controlled automated resources, and tagged metrics for easy viewing and analysis.
Why Use Grafana with Elasticsearch?
Combining Grafana with Elasticsearch allows teams to visualize, explore, and monitor large datasets in real time. It’s a powerful pairing for operational dashboards, log analysis, and performance tracking.
Elasticsearch support in Grafana
Elasticsearch support in Grafana is very exciting, as one of Elasticsearch's major use cases is storing event data and metrics. Hence, it's natural for a tool like Grafana to be used to visualize this data. In this article, we will walk through the step-by-step process of integrating Grafana with an Elasticsearch instance and then perform some queries.
Step-by-Step: Set Up Grafana and Elasticsearch with Docker
We will use Docker to set up a test environment for Grafana and Elasticsearch. We will use the official Docker images available at:
https://hub.docker.com/r/grafana/grafana/
https://hub.docker.com/_/elasticsearch
While Grafana is a great tool for visualization, we will need some extra tools to visualize data sitting in Elasticsearch with Grafana. Elasticsearch doesn’t include any tools for viewing data in a browser out of the box. It uses REST-based interfaces to interact with the data. So the first step is to get a web UI for Elasticsearch.
Try MetricFire now!
Interested in seeing how MetricFire can help you with the process and help you get new organizational insight? Now's the time! Try a free trial or book a demo.
To get a web interface with Elasticsearch, we will use an open-source Elasticsearch UI called Dejavu. Its Docker image is available here:
https://hub.docker.com/r/appbaseio/dejavu/
Here is a very simple Docker Compose file that starts Grafana, Elasticsearch, and Dejavu.
version: '3'
Services:
grafana:
image: grafana/grafana
ports:
- 3000:3000
elasticsearch:
image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-oss:7.0.1
container_name: elasticsearch
environment:
- discovery.type=single-node
- http.port=9200
- http.cors.enabled=true
- http.cors.allow-origin=http://localhost:1358,http://127.0.0.1:1358
- http.cors.allow-headers=X-Requested-With,X-Auth-Token,Content-Type,Content-Length,Authorization
- http.cors.allow-credentials=true
- bootstrap.memory_lock=true
- 'ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx512m'
ports:
- '9200:9200'
- '9300:9300'
# elasticsearch browser
dejavu:
image: appbaseio/dejavu:3.2.3
container_name: dejavu
ports:
- '1358:1358'
links:
- elasticsearch
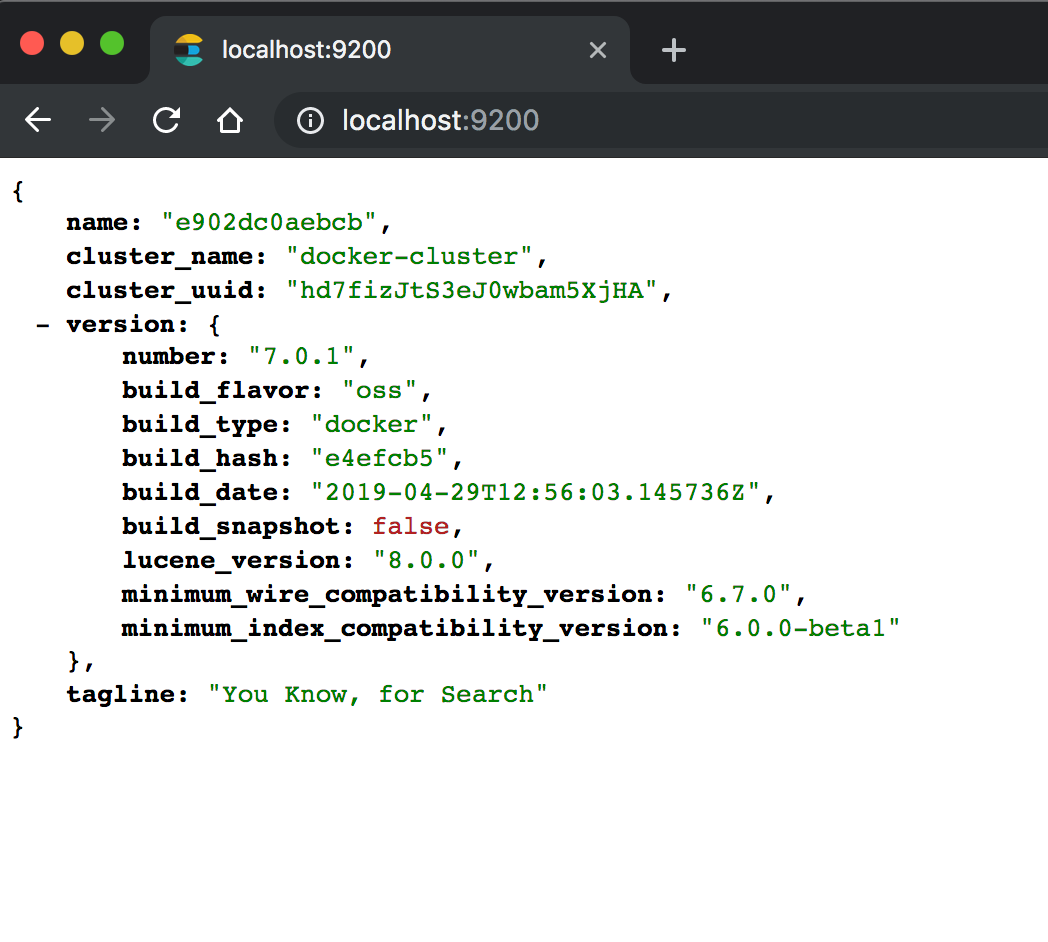
After running this Docker Compose file using docker-compose up -d, browse to http://localhost:9200 to verify that Elasticsearch is up and running. The output should be similar to below.
We will also verify that Grafana is up and running by going to http://localhost:3000. The default credentials are admin/admin.
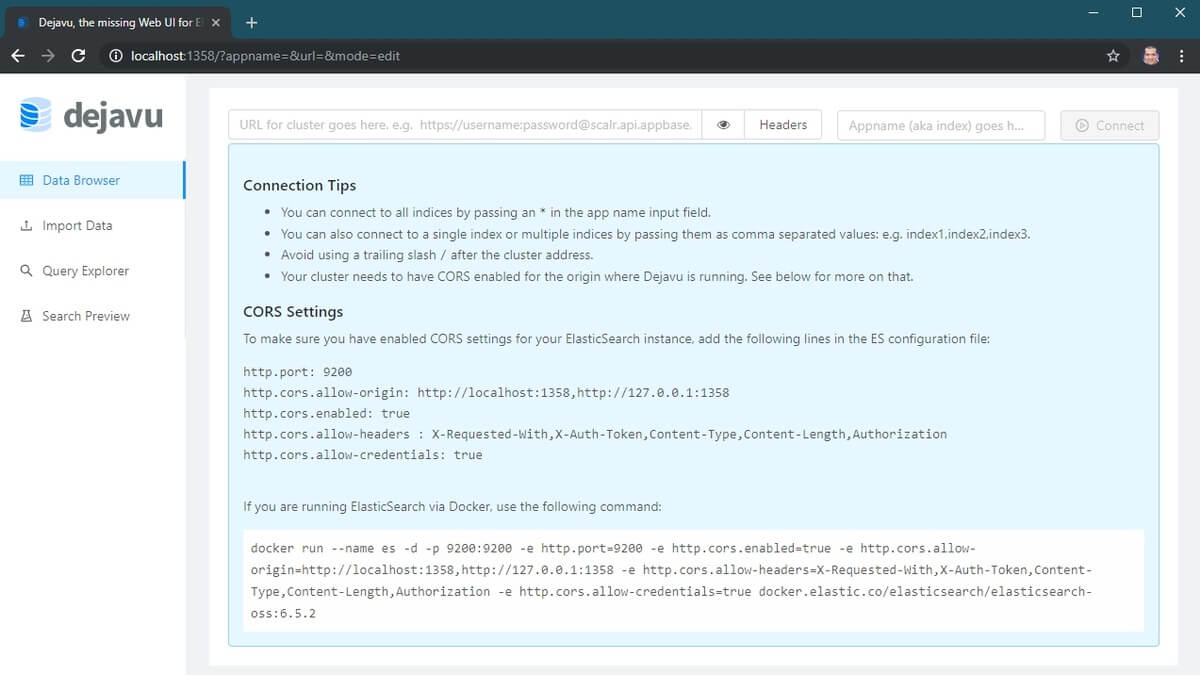
If we go to http://localhost:1358, you’ll see the interface of Dejavu.
Load Sample Data into Elasticsearch
Now, we will import the sample data into Elasticsearch. We’ll simply follow the steps on the official Elasticsearch site to load logs.json data into Elasticsearch.
Specifically, we will execute the following commands:
1. We will download the logs.jsonl file from the elastic servers:
curl -O https://download.elastic.co/demos/kibana/gettingstarted/7.x/logs.jsonl.gz
2. Gunzip the file:
gunzip logs.jsonl.gz
3. And finally, upload to our Elasticsearch instance:
curl -H 'Content-Type: application/x-ndjson' -XPOST 'localhost:9200/_bulk?pretty' --data-binary @logs.jsonl
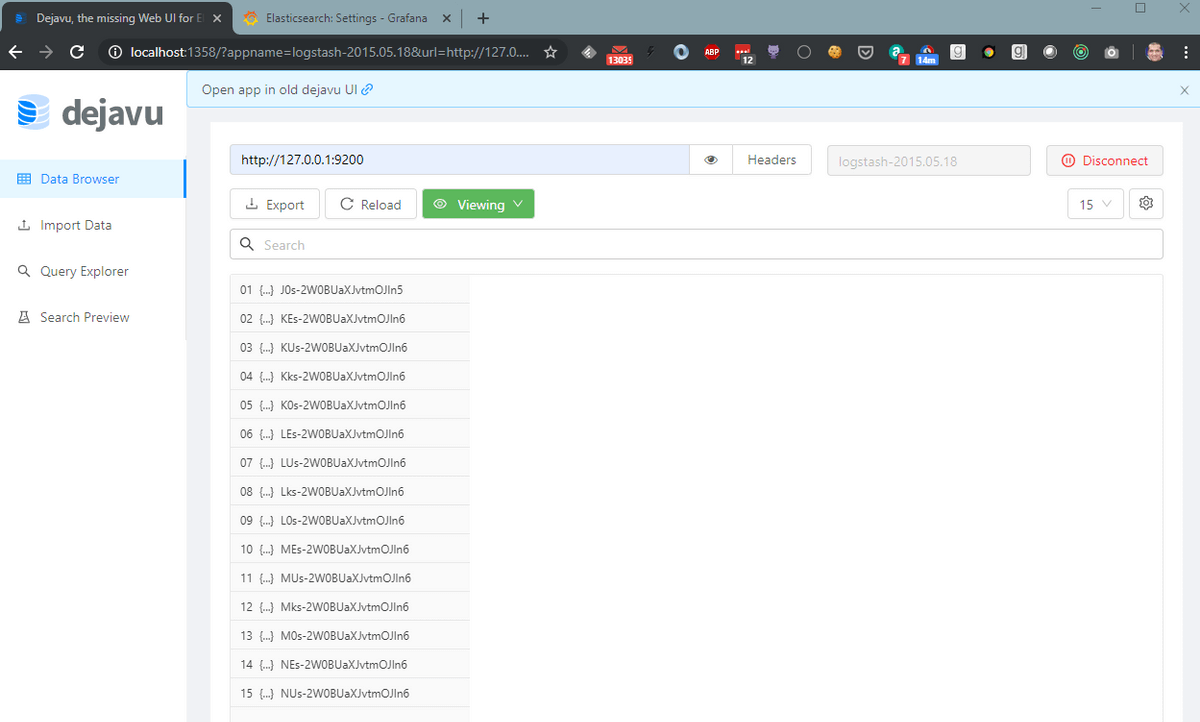
We can confirm the data load by connecting the Dejavu UI to http://127.0.0.1:1358 and logstash-2015.05.18 index:
Connect Grafana to Elasticsearch
Now, for the exciting part. We will connect the Elasticsearch data source to Grafana and create visualizations on top of it.
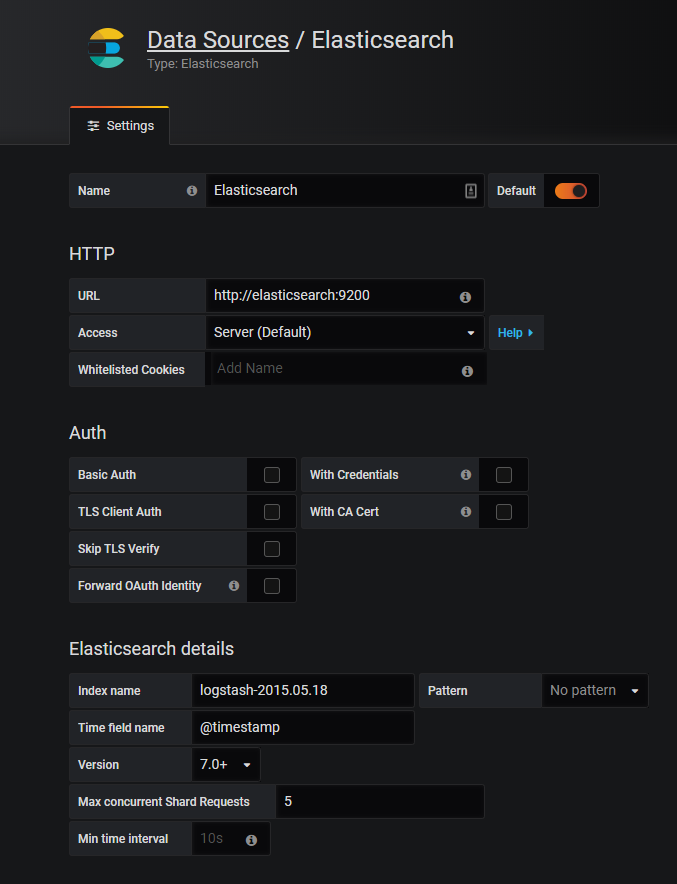
So, head over to Grafana at http://localhost:3000 and add an Elasticsearch data source.
Note: the URL will be http://elasticsearch:9200 if you are using Docker as described in this article. This is because we want Grafana to connect to Elasticsearch from the backend (where it says Access: Server) rather than the browser frontend. For the Grafana container, the Elasticsearch endpoint is http://elasticsearch:9200, not http://127.0.0.1:9200, as you might expect.
The version will be 7.0+, and we will set the Time field name to @timestamp.
Create Grafana Dashboards from Elasticsearch Data
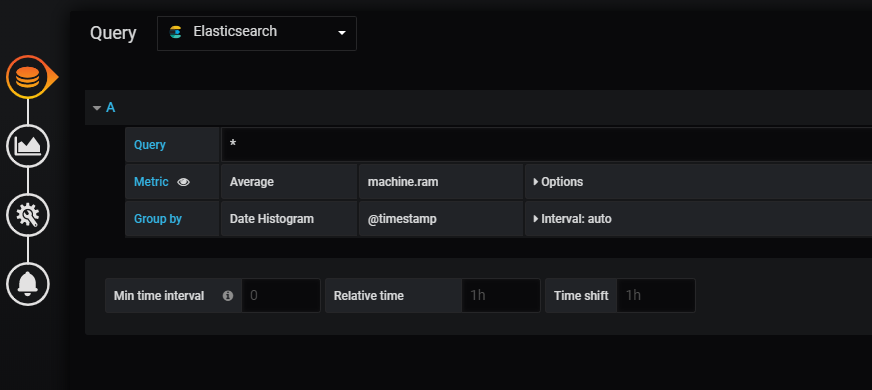
Now, let’s create a simple Grafana dashboard and add a simple graph. This is fairly straightforward. The tricky part is configuring the data source and providing the query.
We will make a visualization of the Average machine RAM from the log data. In the query dropdown box, choose Elasticsearch as the data source, and we will use machine.ram as the average metric, as shown below:
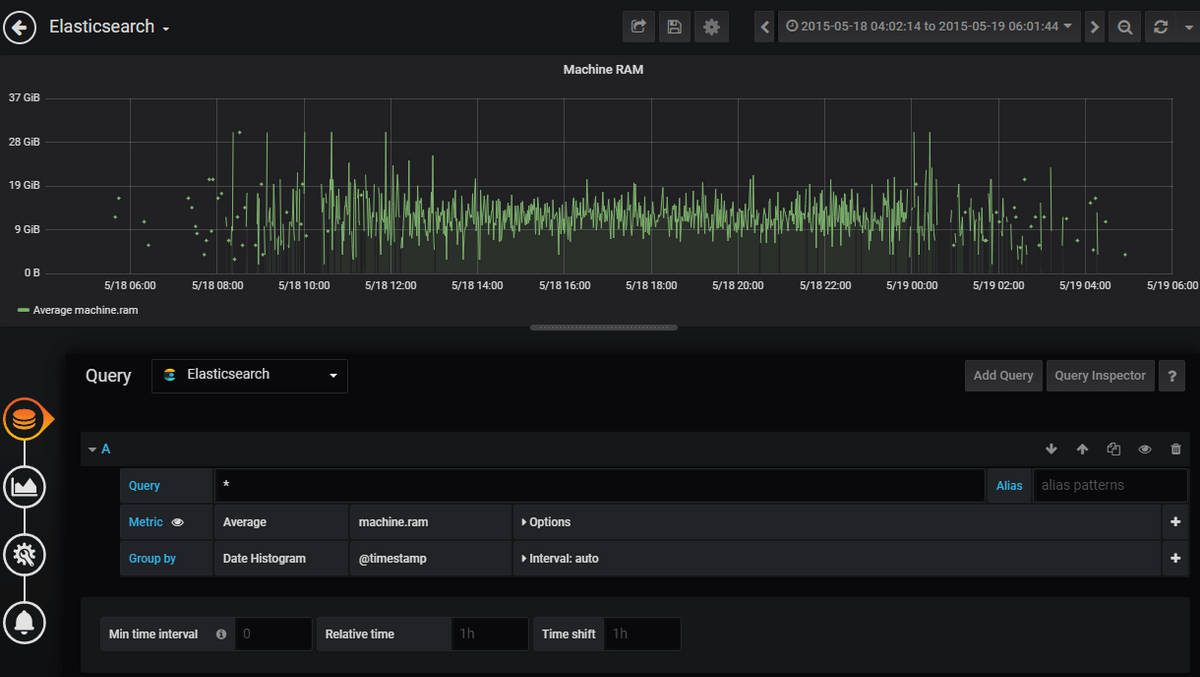
Save the visualization, and we will choose the custom time range in the top right box. This is because our log data contains entries from the month of May 2015. Configuring to this time range gives us the following visualization:
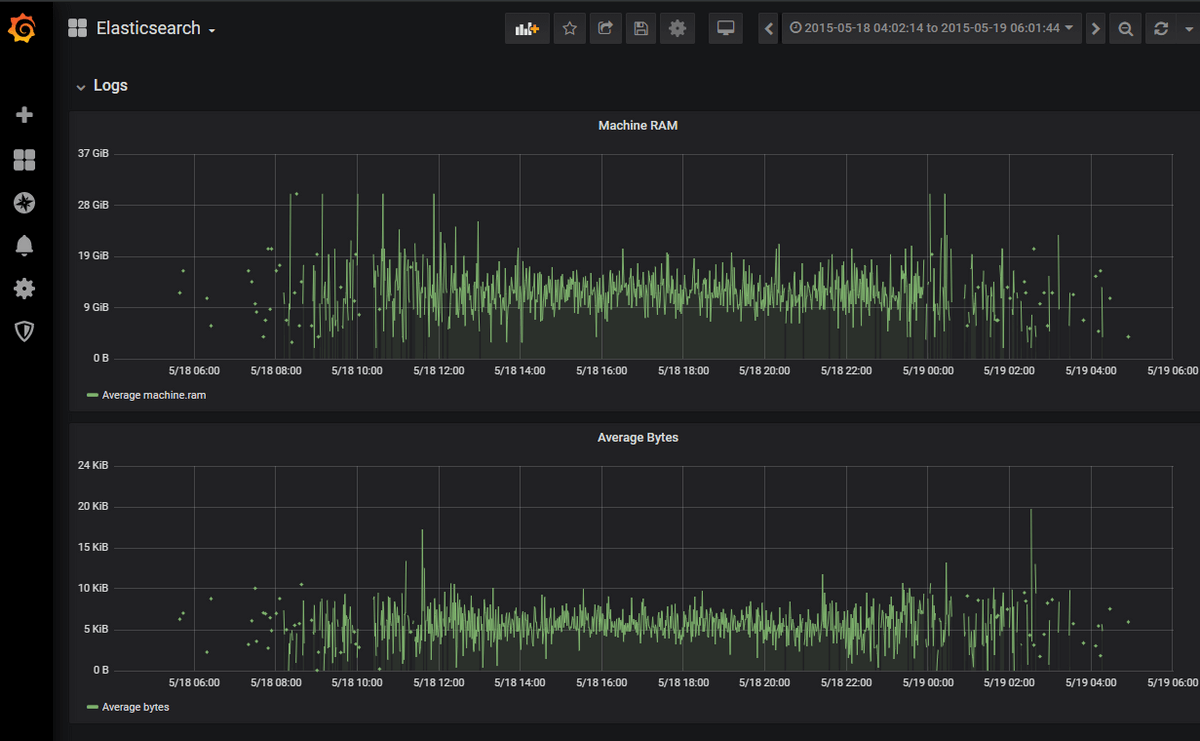
Similarly, I will add the visualization for Average Bytes, and our Grafana dashboard will look like this:
Interested in seeing how MetricFire can help you with the process and help you get new organizational insight? Now's the time! Try a free trial or book a demo.
Troubleshooting Common Elasticsearch + Grafana Issues
If your Grafana dashboard isn’t showing data, check index patterns, time filters, and Elasticsearch mappings. Also, ensure the data source is set to “Server” access mode.
FAQs
Q1: What is Elasticsearch used for?
A: Elasticsearch is an open-source search and analytics engine that indexes structured and unstructured data for lightning-fast search and aggregation.
Q2: Can Grafana connect directly to Elasticsearch?
A: Yes. Grafana supports Elasticsearch as a native data source, allowing you to query, visualize, and monitor your Elasticsearch indices in real time.
Q3: How do I connect Elasticsearch to Grafana using Docker?
A: Run both containers in the same Docker network and use the container name (e.g., http://elasticsearch:9200) as the Grafana data source URL.
Q4: Why use Grafana over Kibana with Elasticsearch?
A: Grafana offers more flexibility in dashboard design, multi-data-source support, and alerting capabilities, while Kibana focuses mainly on Elasticsearch analytics.
Q5: What is MetricFire’s Hosted Grafana?
A: Hosted Grafana by MetricFire is a managed service that simplifies setup, scaling, and plugin management for Grafana dashboards, including Elasticsearch integrations.
Conclusion
Grafana provides a seamless way to connect to the Elasticsearch data. Try MetricFire’s hosted Grafana to explore your own Elasticsearch data in minutes. Also, book a demo and talk to us directly about the best monitoring solution for you.
This post came from our guest blogger Madhur Ahuja. Follow him on Twitter for more great ideas and information about monitoring!