Table of Contents
Great systems are not just built. They are monitored.
MetricFire is a managed observability platform that helps teams monitor production systems with clean dashboards and actionable alerts. Delivering signal, not noise. Without the operational burden of self-hosting.
Introduction
The ELK stack, which stands for Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana, is a powerful suite of tools for searching, analyzing, and visualizing log data in real-time. Within a software company's infrastructure, this stack can be utilized in several key areas to improve operational efficiency, debug issues, and gain insights into user behavior.
The ELK stack provides a centralized platform for aggregating logs from various sources. Logstash can collect and process data from different inputs, Elasticsearch can index and store this data, and Kibana can visualize and analyze the data in real-time. This centralization supports quick debugging, monitoring, and analysis of issues across the entire infrastructure.
So, if an ELK stack is crucial for monitoring the performance of your infrastructure, what about tracking the performance of your ELK stack? That's where MetricFire can help!
In this article, we'll detail how to use the Telegraf agent to collect ELK performance metrics and forward them to a MetricFire account.
Getting Started with the Telegraf Agent
Telegraf is a plugin-driven server agent built on InfluxDB that collects and sends metrics/events from databases, systems, processes, devices, and applications. It is written in Go, compiles into a single binary with no external dependencies, and requires a minimal memory footprint. Telegraf is compatible with many operating systems and has many helpful output plugins and input plugins for collecting and forwarding a wide variety of system performance metrics.
Install Telegraf (Linux/Redhat)
/etc/telegraf/wget https://dl.influxdata.com/telegraf/releases/telegraf_1.30.0-1_amd64.deb
sudo dpkg -i telegraf_1.30.0-1_amd64.deb
RedHat/CentOS
wget https://dl.influxdata.com/telegraf/releases/telegraf-1.30.0-1.x86_64.rpm
sudo yum localinstall telegraf-1.30.0-1.x86_64.rpm
Configure an Output
You can configure Telegraf to output to various sources, such as Kafka, Graphite, InfluxDB, Prometheus, SQL, NoSQL, and more.
In this example, we will configure telegraf with a Graphite output. If you're not currently hosting your data source, start a 14-day free trial with Hosted Graphite by MetricFire to follow these next steps.
A Hosted Graphite account will provide the data source, offer an alerting feature, and include Hosted Grafana as a visualization tool.
To configure the Graphite output, locate the downloaded telegraf configuration file at /etc/telegraf/telegraf.conf and open it in your preferred text editor. Then, you will need to make the following changes to the file:
First, uncomment the line:
[[outputs.graphite]]
Next, uncomment and edit the server line to:
servers = ["carbon.hostedgraphite.com:2003"]
Finally, uncomment and edit the prefix line to:
prefix = "<YOUR_API_KEY>.telegraf"
Configure the Elasticsearch Input Plugin
Telegraf has many input plugins that can collect a wide range of data from many popular technologies and 3rd party sources. In this example, we'll demonstrate how to configure the Elasticsearch plugin.
All you need to do is search for the inputs. Elasticsearch section in your Telegraf.conf file, and uncomment the [[inputs.elasticsearch]] line:
[[inputs.elasticsearch]]
Then you can uncomment the 'servers' line; the default URL is:
servers = ["http://localhost:9200"]
Next, uncomment/modify the following sections in the Elasticsearch plugin config (some can optionally be set to false to limit the number of metrics forwarded):
http_timeout = "5s"
local = true
cluster_health = true
cluster_stats = true
cluster_stats_only_from_master = true
indices_include = ["_all"]
indices_level = "shards"
Save your changes, and then start Telegraf using the following command to see if there are any configuration errors in the output:
telegraf --config telegraf.conf
Telegraf will now be forwarding Elasticsearch metrics to your data source. See our Elasticsearch blog article for additional details or the official GitHub repository for more information and configuration options for the Elasticsearch input plugin.
Configure the Logstash Input Plugin
Telegraf has many input plugins that can collect a wide range of data from many popular technologies and 3rd party sources. In this example, we'll demonstrate how to configure the Logstash plugin.
Within your telegraf.conf file, locate and uncomment the [[inputs.logstash]] line:
[[inputs.logstash]]
Then you can uncomment the 'URL' line; the default path is:
url = "http://127.0.0.1:9600"
Save your changes, and then start Telegraf using the following command to see if there are any configuration errors in the output:
telegraf --config telegraf.conf
Telegraf will now be forwarding Logstash metrics to your data source. See our Logstash blog article for additional details or the official GitHub repository for more information and configuration options for this input plugin.
Configure the Kibana Input Plugin
Telegraf has many input plugins that can collect a wide range of data from many popular technologies and 3rd party sources. In this example, we'll demonstrate how to configure the Kibana plugin.
Open your Telegraf.conf file, and uncomment the [[inputs.kibana]] line:
[[inputs.kibana]]
Then you can uncomment the 'servers' and 'timeout' lines; the defaults are:
servers = ["http://localhost:5601"]
timeout = "5s"
Save your changes, and then start Telegraf using the following command to see if there are any configuration errors in the output:
telegraf --config telegraf.conf
Telegraf will now be forwarding Kibana metrics to your data source. See our Kibana blog article for additional details or the official GitHub repository for more information and configuration options for the Elasticsearch input plugin.
Use Hosted Graphite by MetricFire to Create Custom Dashboards and Alerts
MetricFire is a monitoring platform that enables you to gather, visualize, analyze, and alert on metrics from sources such as servers, databases, networks, devices, and applications. Using MetricFire, you can effortlessly identify problems and optimize resources within your infrastructure. Hosted Graphite by MetricFire removes the burden of self-hosting your monitoring solution, allowing you more time and freedom to work on your most important tasks.
- Once you have signed up for a Hosted Graphite account and used the above steps to configure your server with the Telegraf Agent, metrics will be forwarded, timestamped, ingested, and aggregated into the Hosted Graphite backend.
- They will be sent and stored in the Graphite format of metric.name.path <numeric-value> <unix-timestamp> provides a tree-like data structure and makes them easy to query.
- Now that all of your ELK performance metrics are in 1 place, you can locate them in your Hosted Graphite account and use them to build custom Dashboard Alerts.
Create Dashboards in Hosted Graphite's Hosted Grafana
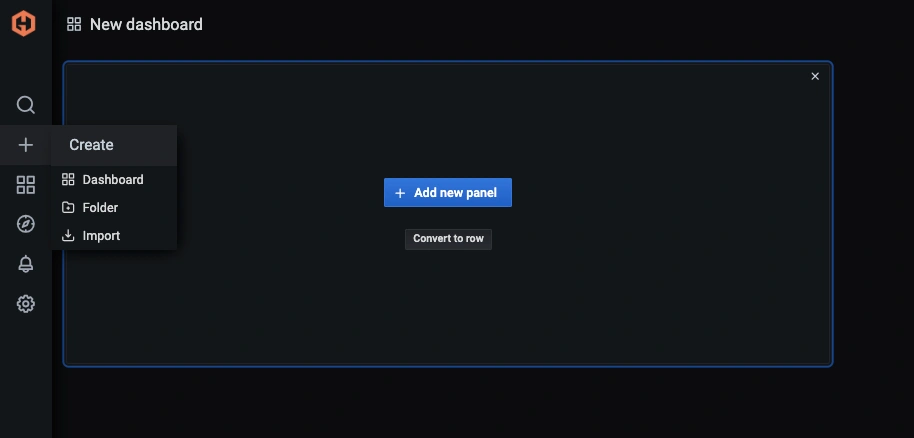
In the Hosted Graphite UI, navigate to Dashboards => Primary Dashboards and select the + button to build new panels:
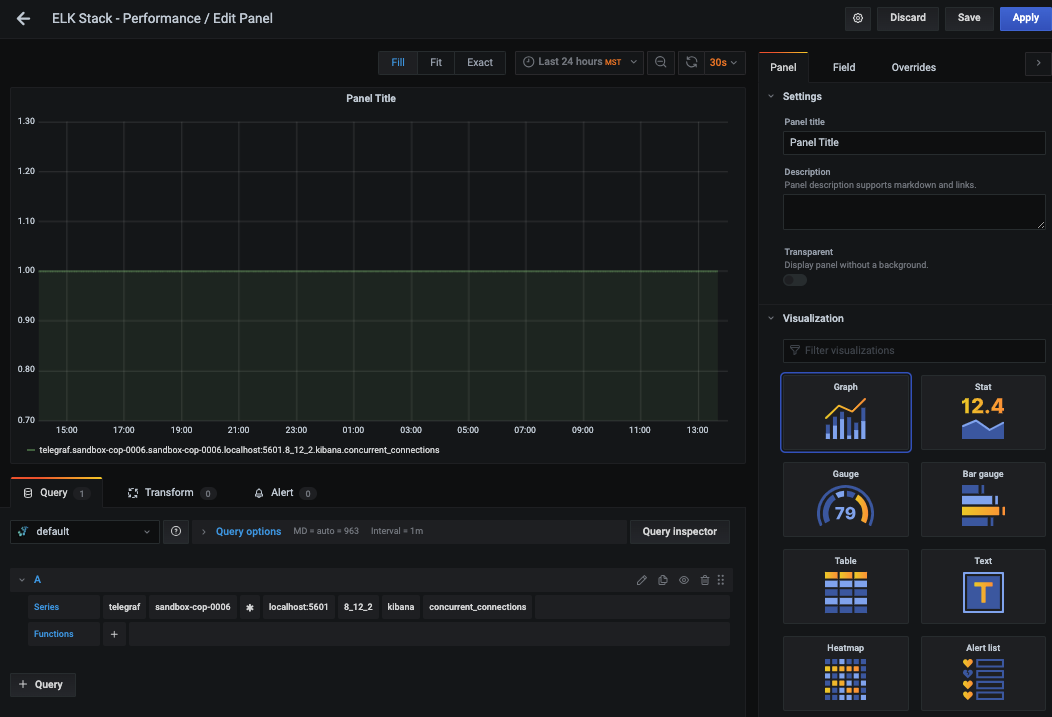
Then you can go into Edit mode and use the query UI to select a graphite metric path:
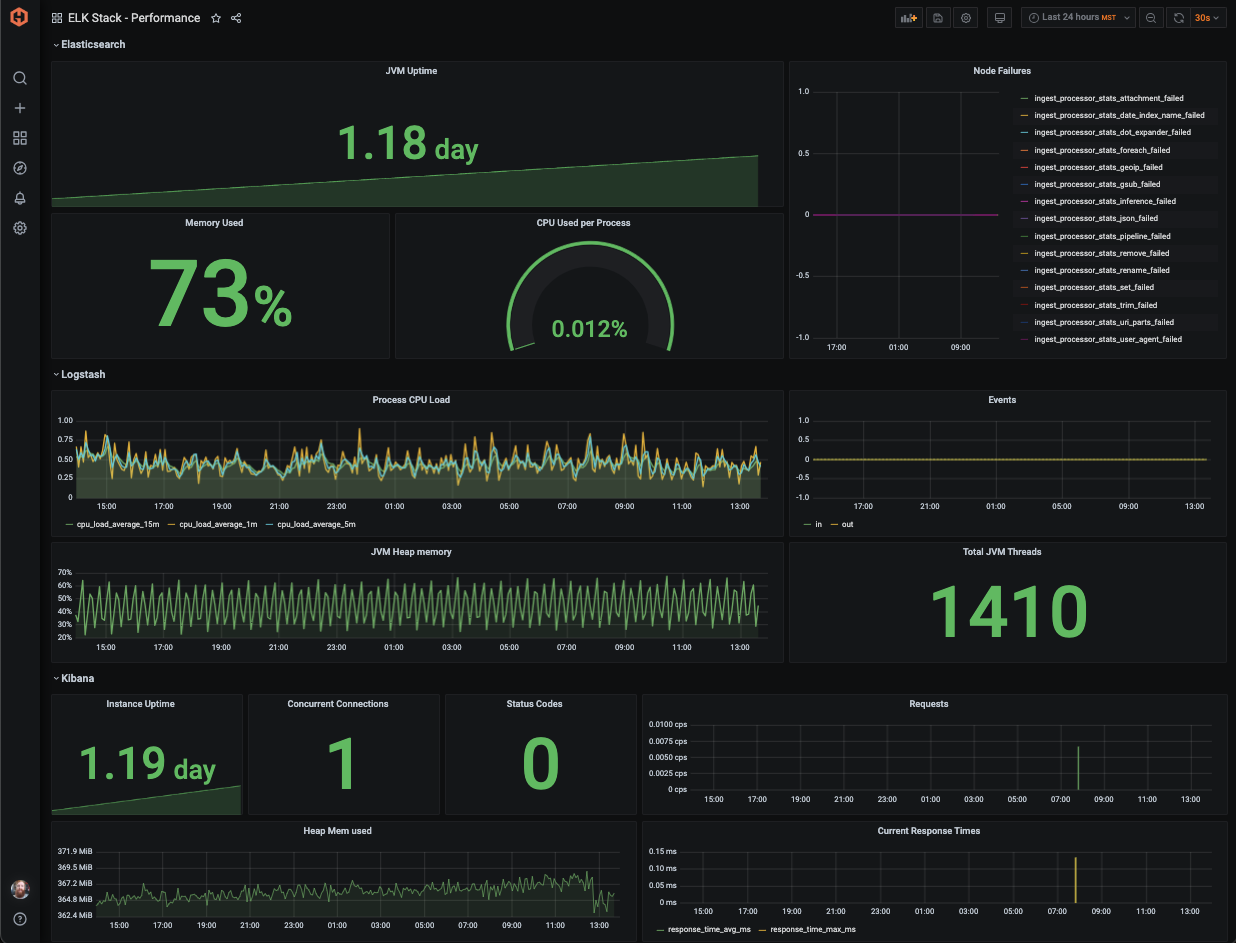
Here's an example of how you might visualize your Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana metrics on the same dashboard:
See the Hosted Graphite dashboard docs for more details on creating dashboards and adding advanced features like Graphite Functions, Dashboard Variables and Annotations.
Creating Graphite Alerts
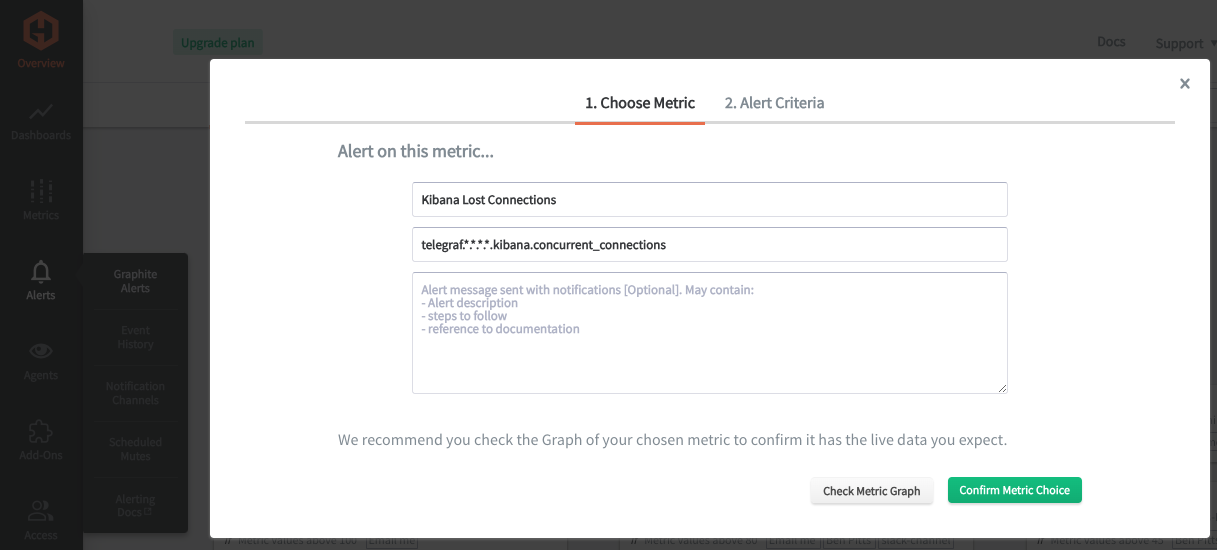
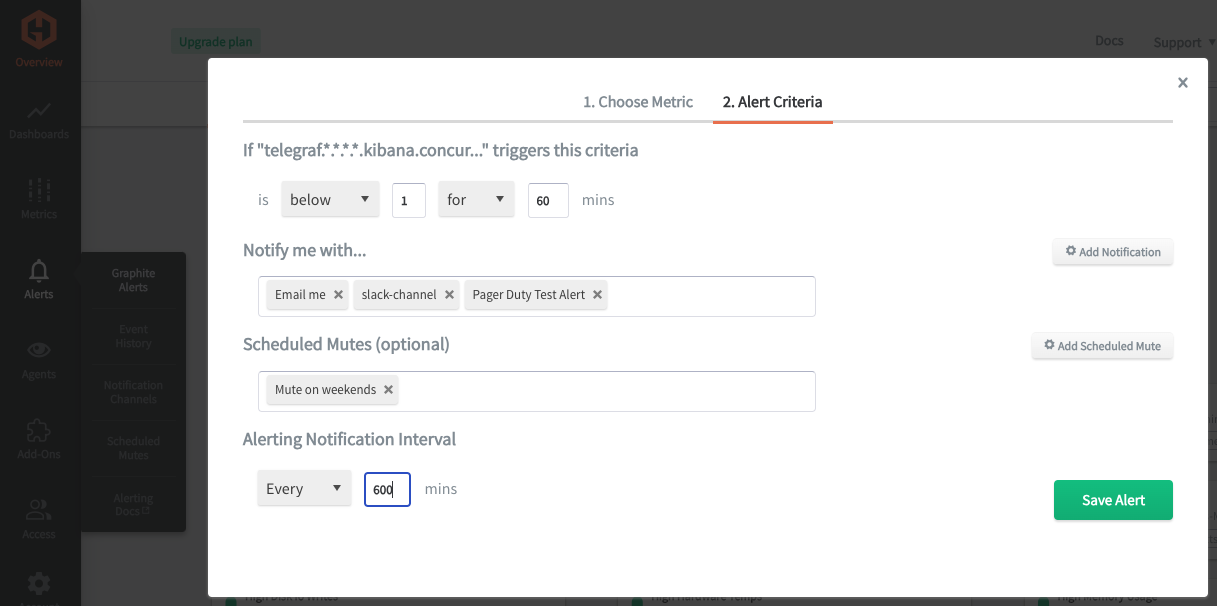
In the Hosted Graphite UI, navigate to Alerts => Graphite Alerts to create a new alert. Name the alert, add one of your graphite metrics to the alerting metric field, and add a description of what this alert is:
Then select the Criteria tab, which will set the threshold, and select a notification channel:
NOTE: the default notification channel is the email you used to sign up for the Hosted Graphite account, but you can easily configure a channel for Slack, PagerDuty, Microsoft Teams, and more. See the Hosted Graphite docs for more details on notification channels.
Conclusion
Monitoring the performance of your ELK stack is vital for ensuring that critical logging, monitoring, and data analysis functions operate efficiently and without interruption. This directly impacts your business's ability to make informed decisions and maintain high operational standards. It also helps optimize resource usage, preemptively identifying issues and safeguarding against data loss or security breaches, supporting overall business continuity and performance.
Tools like dashboards and alerts complement this monitoring by providing real-time visualization, proactive identification of issues, historical trend analysis, and facilitating informed decision-making, all essential for maintaining a robust and efficient infrastructure.
Sign up for a free trial, and start monitoring your ELK infrastructure today! You can also book a demo and talk to the MetricFire team directly about your monitoring needs.